Vector Potential Variation Method application to
cylinder quantum dot energy spectrum calculation
Alexej Ivanovich Ivanov and Olga Rudolfovna Lobanova*
Physical Department, Kaliningrad State University,
Kaliningrad, 236041 Russia
This is an abstract
for a presentation given at the
11th
Foresight Conference on Molecular Nanotechnology
In present work has been investigated application of vector potential variation method to energy spectrum calculation of one electron cylinder quantum dot in weak homogeneous magnetic field. External magnetic field was directed perpendicular to the cylinder axis.
Earlier vector potential variation method was successfully applied to calculation of proton nuclear magnetic shielding constants in diatomic molecules [1].
This method allows to come from the definition problem of correction wave function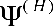 , linear relatively external magnetic field, to the determination problem of such vector potential , linear relatively external magnetic field, to the determination problem of such vector potential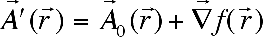 , (where , (where 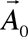 is fixed vector potential, describing external magnetic field is fixed vector potential, describing external magnetic field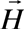 , f- gradient transformation function ) for which correction wave function , f- gradient transformation function ) for which correction wave function 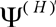 turns into zero. Hence calculation of corrections to energy and other characteristics, caused by external magnetic field, is reduced to calculation of corresponding diamagnetic quantities. Vector potential, satisfying this property, is named natural vector potential turns into zero. Hence calculation of corrections to energy and other characteristics, caused by external magnetic field, is reduced to calculation of corresponding diamagnetic quantities. Vector potential, satisfying this property, is named natural vector potential 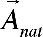 . Equation for natural vector potential has a look . Equation for natural vector potential has a look
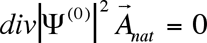 , ,
which can be obtained from the first orderequation of perturbation theory for correction wave function. Exact solution of equation for natural vector potential 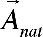 in finite look is possible only in simplest cases (for example, in case of anisotropic harmonic oscillator). Therefore, usually is determined some approximation to in finite look is possible only in simplest cases (for example, in case of anisotropic harmonic oscillator). Therefore, usually is determined some approximation to 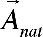 , varying f in some limited class of functions. , varying f in some limited class of functions.
Rebane T.K. [2] has formulated energy variation prin ciple, which allows to obtain optimum look of gradient transformation function. Diamagnetic correction to energy, corresponding to some vector potential 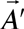 from family from family 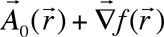 , has a look , has a look
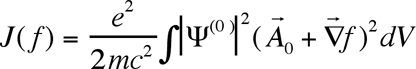 . .
Value J(f) is functional relatively gradient transformation function f. From the stationary condition of this functional 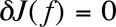 is defined equation for gradient transformation function. is defined equation for gradient transformation function.
Gradient transformation function, used in this calculation, correspond to circular approximation 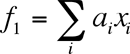 and elliptic approximation and elliptic approximation 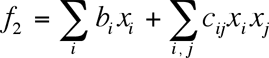 , where , where 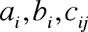 are variation parameters, are variation parameters, 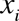 are electron cartesian coordinates. are electron cartesian coordinates.
Obtained values of corrections to cylinder quantum dot energy, caused by external magnetic field, are small.
Results, obtaining in elliptic and circular approximations to natural vector potential 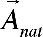 , weakly differ from each other. Implemented calculations show that vector potential variation method can be applied to energy spectrum calculation of quantum dot structures in weak magnetic fields. , weakly differ from each other. Implemented calculations show that vector potential variation method can be applied to energy spectrum calculation of quantum dot structures in weak magnetic fields.
References
[1] Rebane T.K., Vestnik Leningradskogo Universiteta, π4, Ò. 38-45. (1973)
[2] Rebane T.K., JETP 38, v.3, 963 965 (1960)
Abstract in RTF format 222,904 bytes
*Corresponding Address:
Olga Rudolfovna Lobanova
Physical Department, Kaliningrad State University
Al.Nevsky st.14
Kaliningrad, 236041 Russia
Phone: 8 (0112) 33 82 17 Fax: 8 (0112) 465813
Email: [email protected]
|