Analysis of multiple diffraction images provides high contrast, high quality, full field 3D imaging of surfaces illuminated by extreme ultraviolet photons from a tabletop laser.
Femtosecond imaging with near nanometer spatial resolution


Analysis of multiple diffraction images provides high contrast, high quality, full field 3D imaging of surfaces illuminated by extreme ultraviolet photons from a tabletop laser.
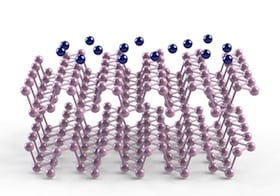
A vertical electrical field from dopant atoms of potassium added to the surface of a few stacked layers of phosphorene tunes the band gap of black phosphorous, possibly leading to novel electronic and optoelectronic devices.
A new set of design rules enables constructing any wireframe nanostructure, which may lead to new medical applications and new nanomachines.
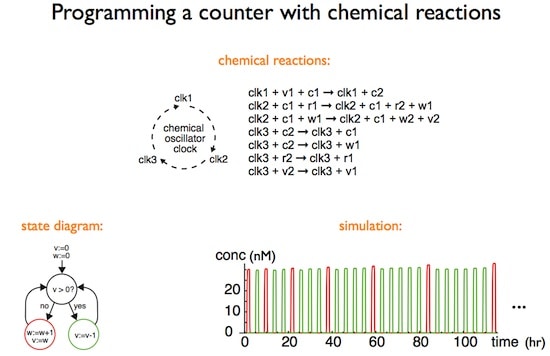
Modeling DNA strand displacement cascades according to three simple rules can in principle mimic the temporal dynamics of any other chemical system, presenting a method to model regulatory networks even more complicated than those of biology.
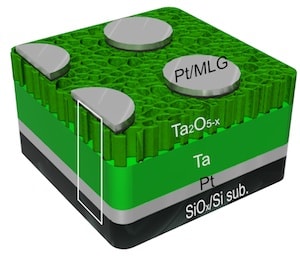
A novel nanostructured material based on tantalum oxide could make possible non-volatile crossbar array memories that store up to 162 gigabits in 3-D memory stacks.

Functional ribosomes with subunits engineered to not separate at the completion of each protein translation cycle make possible engineering systems to make a variety of novel polymers with novel properties.

An automated design process folds arbitrary meshes to produce DNA origami structures difficult to design by previous methods, including more open structures that are stable in ionic conditions used in biological assays.

Nanobreadboards made of DNA bricks provide twice the positional precision, twice the packing density, and faster prototyping than do alternative means to arrange functional molecules.

Recent research demonstrates that certain non-aqueous solvents can not only be used to assemble DNA nanostructures, but offer certain advantages over conventional aqueous solvents.