The directed, artificial evolution of genes for enzymes that produce nanoparticles of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide produced semiconductor structures not seen in nature.
Artificial evolution of enzymes to make novel semiconductors
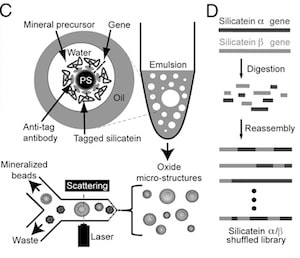

The directed, artificial evolution of genes for enzymes that produce nanoparticles of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide produced semiconductor structures not seen in nature.
Nanotechnology combines an enzyme and a DNA molecule on the surface of gold nanoparticles to destroy hepatitis C virus in human cells and in a mouse model of disease.
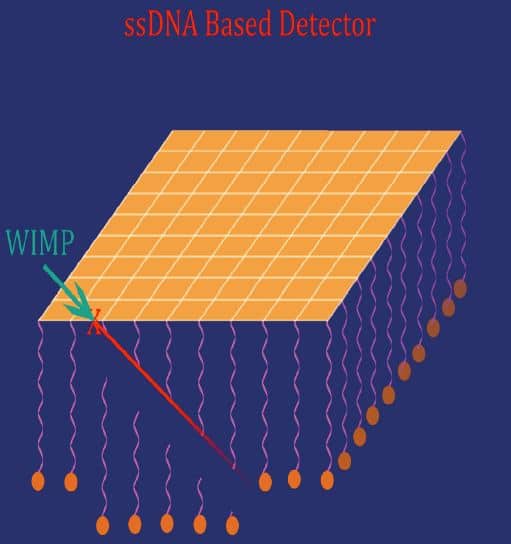
A forest of long DNA strands hanging at known positions from a thin gold foil may provide a method to detect hypothetical particles of dark matter, thought to compose 26% of the universe.
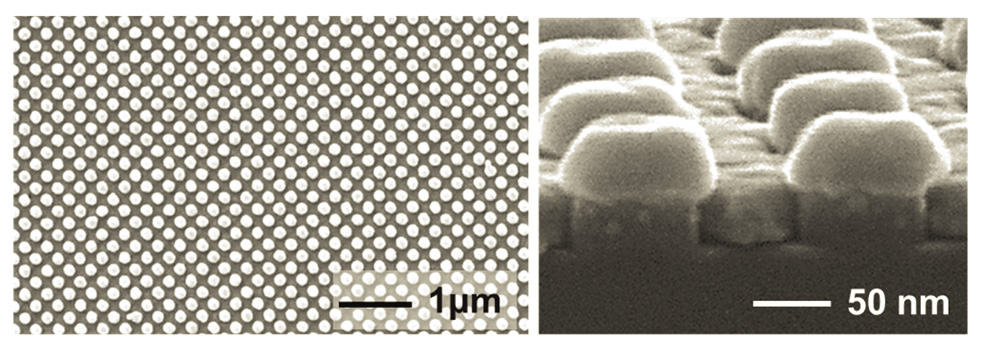
A new nanomaterial provides a three million-fold improvement in the sensitivity of common medical tests, potentially permitting earlier detection of cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
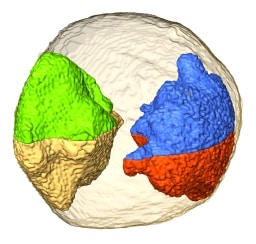
Current methods can image individual atoms in complex structures if the structures are crystalline, comprising many identical structures in a regular array. A new method resolves individual atoms in nanoparticles comprising several irregularly arranged crystalline grains.

Zyvex Technologies and ENVE Composites have demonstrated the superiority of a proprietary nanostructured composite in downhill cycling.
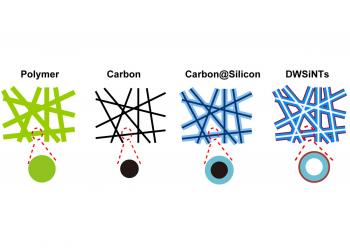
Templates made from polymer nanofibers enable the formation of long-lived silicon nanostructures that store ten times as much charge as do graphite battery terminals.

Nanoparticles targeted to cancer cells by antibodies cannot achieve enough specificity to kill drug-resistant cancer cells while sparing normal cells, but can achieve enough specificity to produce nanobubbles only in cancer cells, so the drug only enters cancer cells.

Doping carbon nanotubes with boron while they are being formed produces a novel molecular architecture formed by boron induced kinks and linkages. These nanosponges can be used repeatedly to absorb and retrieve or burn spilled oil.
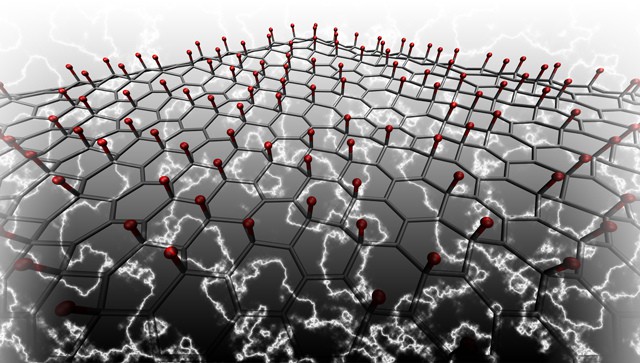
Calculations using density functional theory have demonstrated that graphene can be made piezoelectric by adsorbing atoms or molecules on one surface, or by adsorbing different atoms or molecules on each surface.