Nanotechnology combines an enzyme and a DNA molecule on the surface of gold nanoparticles to destroy hepatitis C virus in human cells and in a mouse model of disease.
Nanotechnology combines an enzyme and a DNA molecule on the surface of gold nanoparticles to destroy hepatitis C virus in human cells and in a mouse model of disease.

A new online game allows players to design RNA molecules. The most promising designs are synthesized, and the players given real-world feedback on how well their designs worked.

Nanoparticles made from specific DNA and RNA strands, homogeneous in size, composition, and surface chemistry, proved superior to other nanoparticles in silencing gene expression in tumors in mouse experiments.
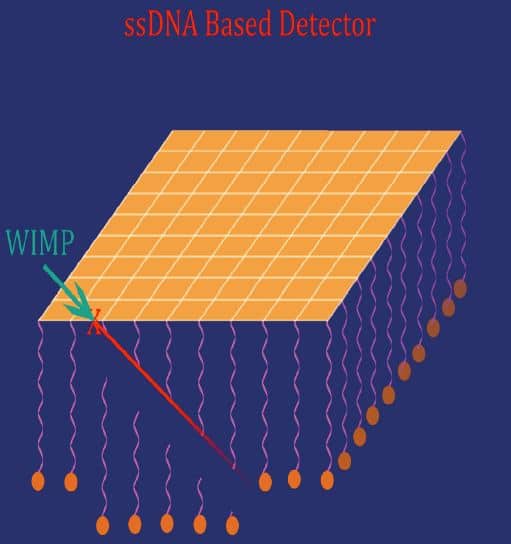
A forest of long DNA strands hanging at known positions from a thin gold foil may provide a method to detect hypothetical particles of dark matter, thought to compose 26% of the universe.

The demonstration that the process of DNA replication is more flexible than thought should make it easier to incorporate unusual amino acids into designed proteins, which might make it easier to design novel protein machines.
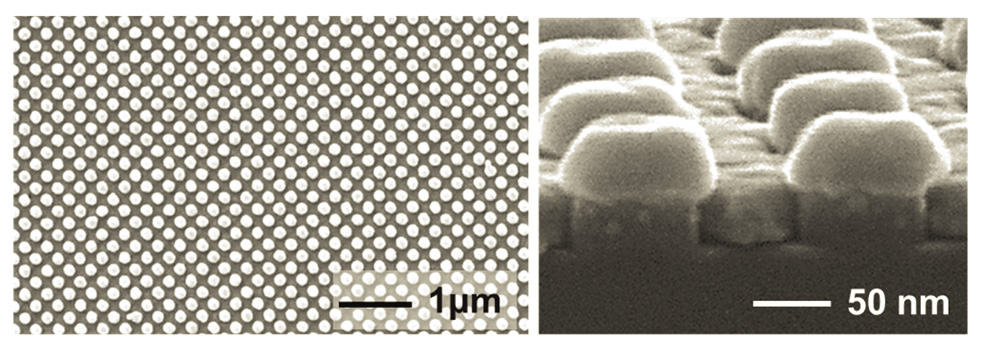
A new nanomaterial provides a three million-fold improvement in the sensitivity of common medical tests, potentially permitting earlier detection of cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
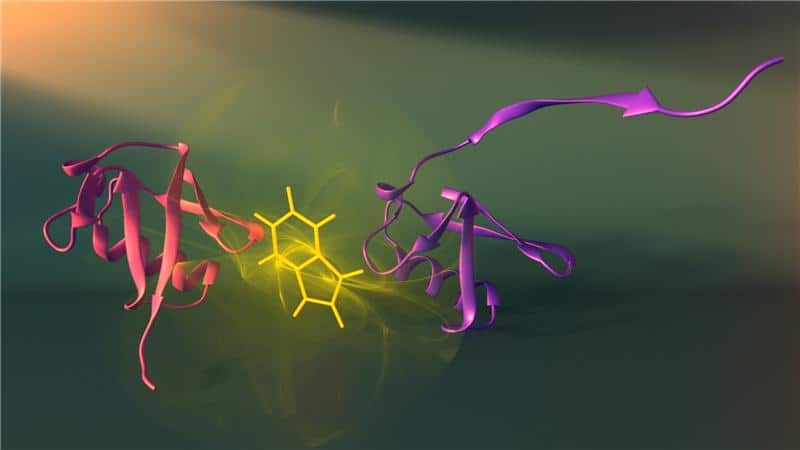
Tryptophan residues introduced at various positions in a protein chain identify folding intermediates that are too short-lived to be structurally characterized otherwise.

A variety of protein cage structures have been constructed by designing specific protein domains to self-assemble as atomically precise protein building blocks in defined geometries.

A set of 310 short single-stranded DNA tiles, plus a few additional short sequences for the edges, has been used to form more than a hundred large, complex DNA objects.

Darpa has launched a “Living Foundries” program to bring an engineering perspective to synthetic biology to greatly accelerate progress through standardization and modularization.