A new set of design rules enables constructing any wireframe nanostructure, which may lead to new medical applications and new nanomachines.
Novel wireframe nanostructures from new DNA origami design process
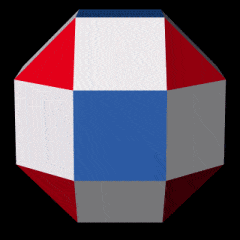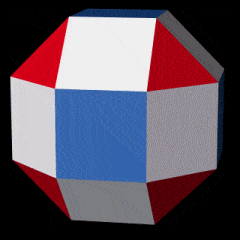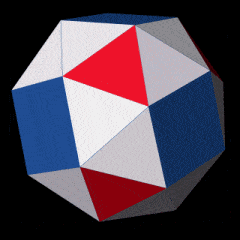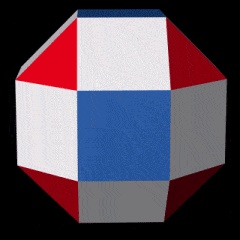

A new set of design rules enables constructing any wireframe nanostructure, which may lead to new medical applications and new nanomachines.
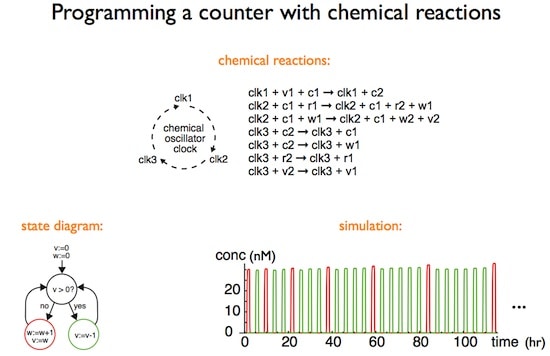
Modeling DNA strand displacement cascades according to three simple rules can in principle mimic the temporal dynamics of any other chemical system, presenting a method to model regulatory networks even more complicated than those of biology.
Designing and building spiroligomers, robust building blocks of various 3D shapes made from unnatural amino acids, decorated with various functional groups, and linked rigidly together by pairs of bonds, and a new approach to nanotechnology design software.
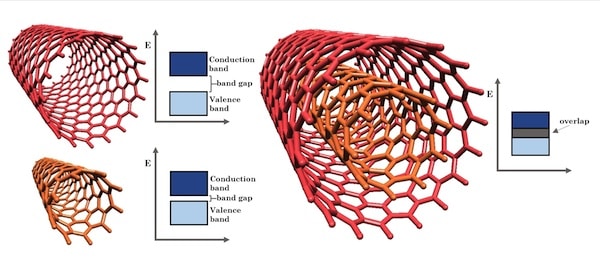
Density functional theory calculations of the electronic properties of double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWCNTs) comprising two concentric zigzag tubes of different chiralities reveal complex effects upon the electronic band gap, identifying candidate combinations for diverse applications from transistors to macroscopic conducting wires.
A combination of techniques has made possible the expansion of problems that can be handled by first-principles molecular dynamics from a few hundred atoms to a very large system containing 32,768 atoms.

At the 2013 Conference Dean Astumian contrasted macroscopic machines at static equilibrium and molecular machines at dynamic equilibrium, and presented information ratchets and microscopic reversibility as the organizing principle of molecular machines.

At the 2013 Conference Gerhard Klimeck presented the work of his computational nanotechnology network modeling nanoelectronic devices, using simulations of multi-million atom domains to understand the function of single atom devices embedded in larger nanostructures.
A new form of carbon produced by very slowly releasing benzene compressed at 200,000 times atmospheric pressure may be the strongest material possible.

The Theory Prize was given for research into diamond nanoparticles; the Experimental Prize was given for development of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) technology.
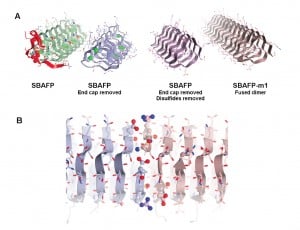
Design and computational simulation of amyloid proteins of diverse functions from diverse sources enable the self-assembly of proteins that could provide scaffolds for diverse applications.