A collection of open access journals on a variety of topics provides a very useful entry point to the rapidly growing collection of scientific, technical, and scholarly research that is not hidden behind pay walls.
A collection of open access journals on a variety of topics provides a very useful entry point to the rapidly growing collection of scientific, technical, and scholarly research that is not hidden behind pay walls.

Using DNA nanotechnology to control and organize molecular motors and the molecular tracks that they run on, a novel nanotrain transports molecular cargos tens of micrometers.

A new book by Frank Boehm explores the challenges, possibilities, and visions of nanomedical device and systems design.
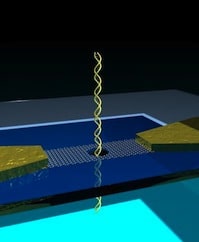
A nanoribbon transistor no thicker than the distance between adjacent DNA bases provides high resolution sensing of DNA passage through nanopores, perhaps leading eventually to rapid DNA sequencing.
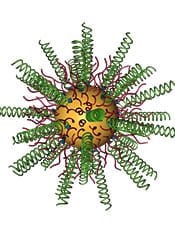
Gold nanoparticles densely coated with RNA molecules intended to silence a gene essential for an incurable brain cancer proved effective in mice engrafted with human glioblastoma multiforme tumor.
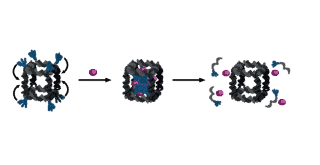
Modifying DNA strands with lipid-like molecules opens more possibilities for designing DNA structures for drug delivery and other purposes.
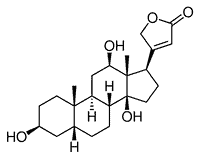
A major advance in the computational design of proteins that bind tightly to specific small molecules will facilitate several technologies, possibly including the development of atomically precise manufacturing.

Nanotechnology draws from physics, chemistry, engineering, computation, etc., and this multi-disciplinary nature has served as a major speed bump in achievement of envisioned nanotech goals. There has been substantial concern that the U.S. is lagging behind other countries in nanotech R&D. Now researchers, companies, and politicians are coming together to create a much-needed physical hub… Continue reading Building a hub for nanotech advancement
How complex could circuits be made using precisely positioned DNA nanostructures as templates to grow graphene nanoribbons?

“Molecular threading”, a nanotechnology developed by Halcyon Molecular and now owned by Aeon Biowares, enables precise placement of individual long molecules of DNA, either for sequencing or for nanofabrication of novel DNA nanostructures.