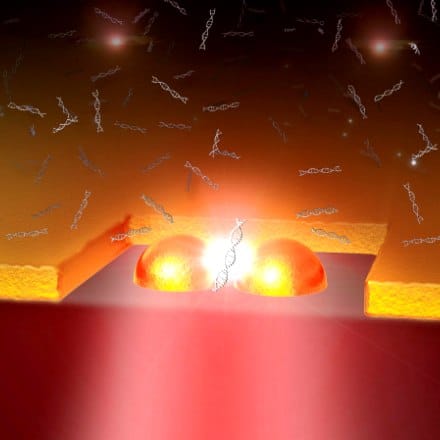
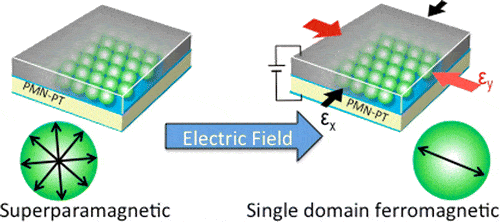
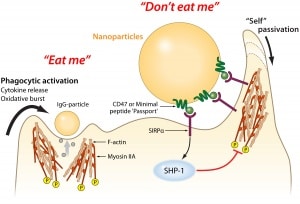
In simplest terms, cellular automata can be thought of as groups of ‘cells’ in which the state of an individual cell will flip depending on the states of its neighbors. A ‘cell’ can be a pixel, a molecule, etc. The mathematical rules associated with cellular automation are complex and have been applied to fields as… Continue reading Improved molecular targeting via cellular automata