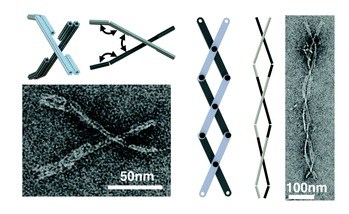
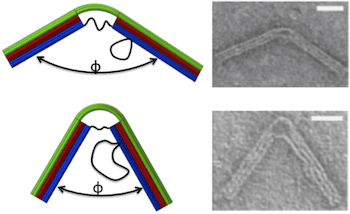
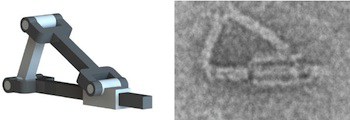
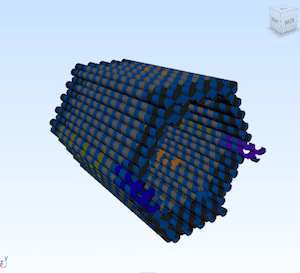
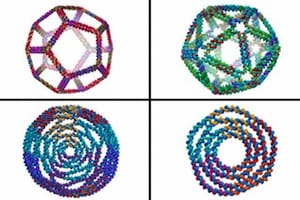
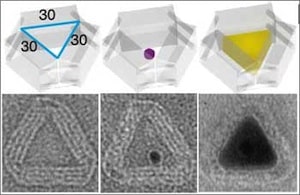
An automated design process folds arbitrary meshes to produce DNA origami structures difficult to design by previous methods, including more open structures that are stable in ionic conditions used in biological assays.
Automated design of polyhedral meshes for DNA origami