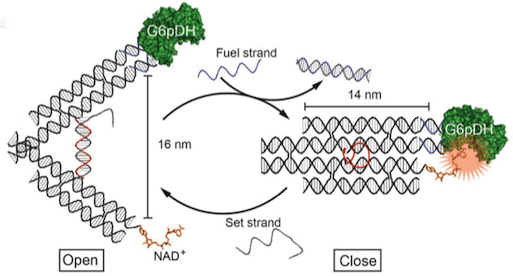
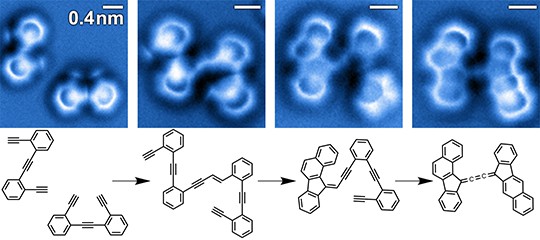
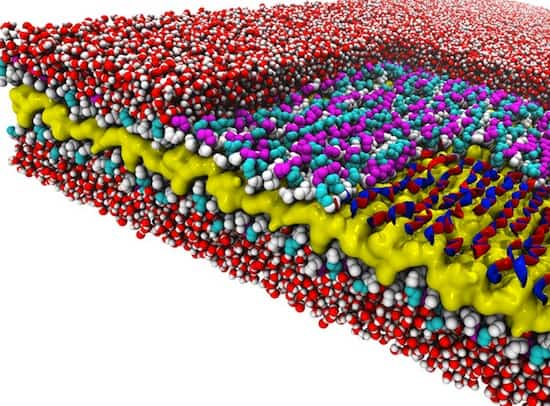
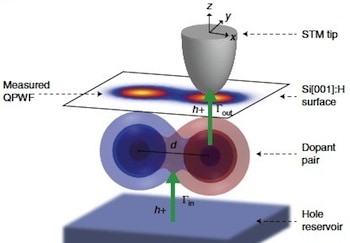
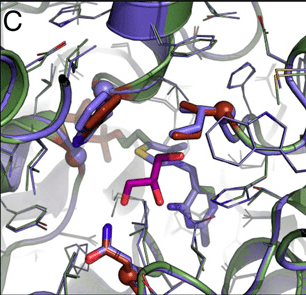
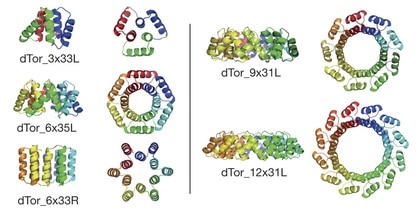
Recent research documents a structure-based rational design strategy combining molecular dynamics and single molecule imaging to improve the performance of a DNA tweezers that accurately positions an enzyme and its cofactor.
Rational improvement of DNA nanodevice function